Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, has been widely used as a cosmetic treatment for over two decades to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles. But how exactly does Botox prevent wrinkles from deepening over time?
When we frown, smile, or express emotions, our facial muscles contract and release, causing the skin above these muscles to fold and crease, resulting in wrinkles. Botox works by injecting a small amount of botulinum toxin into specific muscle groups, temporarily blocking nerve signals that cause muscle contractions.
- By inhibiting muscle contractions, Botox reduces the frequency and severity of wrinkle formation
- It also decreases the elasticity of the skin, reducing its ability to snap back into place after contraction
- The toxin’s effects on the muscles lead to a decrease in skin surface area, making wrinkles appear less pronounced over time
- Botox can also reduce the formation of new wrinkles by decreasing the tension in facial muscles, leading to a smoother appearance
When used consistently and correctly, Botox’s anti-aging properties lead to several long-term benefits. For example:
- The skin’s natural collagen production is stimulated, leading to improved elasticity and texture
- Wrinkle depth and severity decrease over time, as the muscles relax and the skin regains its natural tone
- The risk of new wrinkle formation is reduced, resulting in a more even and youthful appearance
- The overall appearance of fine lines and wrinkles becomes less prominent, giving the skin a smoother and more radiant look
It’s worth noting that Botox’s anti-aging effects are temporary, lasting anywhere from three to six months, depending on individual factors. To maintain its benefits, treatments need to be repeated regularly.
Additionally, while Botox is not a permanent solution for wrinkles, it can be used in conjunction with other anti-aging treatments, such as fillers or chemical peels, to enhance its effects and create a more comprehensive skincare routine.
Botox’s ability to prevent wrinkles from deepening over time has been extensively studied, and the results are clear: when used correctly and consistently, Botox can lead to significant improvements in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, giving patients a smoother, more youthful-looking complexion.
Botox is a popular and highly effective treatment for preventing wrinkle deepening, and its mechanism of action is fascinating.
- Botox contains a neurotoxin protein called botulinum toxin type A, which is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
- This toxin is released when food is not digested properly in the stomach and intestines, but its use in Botox treatment is highly controlled and carefully regulated.
The active ingredient in Botox works by temporarily paralyzing muscles that cause wrinkles to form.
- When Botox is injected into a muscle, it blocks the release of a chemical signal called acetylcholine, which is necessary for muscle contraction.
- This blockade prevents the muscle from contracting and causing wrinkles, resulting in a smoother appearance.
The effects of Botox are achieved through a process called “muscle inhibition,” where the toxin blocks the nerve signals that control muscle movement.
- By inhibiting the muscles responsible for wrinkle formation, such as the crow’s feet, frown lines, and forehead lines, Botox reduces the appearance of wrinkles over time.
- The effects of Botox typically last between 3 to 6 months, after which the muscle activity returns to normal and the wrinkles start to reappear.
It’s worth noting that the mechanism of action of Botox is not fully understood and is still being researched, but its effectiveness in preventing wrinkle deepening is well established.
- Studies have shown that repeated use of Botox can lead to long-term results, with some patients experiencing a significant reduction in wrinkle depth over time.
- The combination of Botox with other treatments, such as fillers and skin rejuvenation therapies, can enhance its effectiveness and provide longer-lasting results.
In addition to its wrinkle-preventing properties, Botox has also been used to treat a range of other medical conditions, including excessive sweating, migraines, and dystonic spasms.
Neurotransmitter Regulation
Botox prevents wrinkles from deepening over time by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically the release of _acetylcholine_, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction and relaxation.
The process begins with the injection of Botox into the facial muscles responsible for wrinkling. Once inside, the botulinum toxin blocks the release of _acetylcholine_ from the nerve terminals, thereby preventing the muscles from contracting and causing wrinkles to deepen.
The regulation of _acetylcholine_ is essential for maintaining proper muscle function. When _acetylcholine_ binds to its receptors on the muscle cells, it triggers a series of events that lead to muscle contraction. In the case of Botox, this process is halted, preventing the muscles from contracting and relaxing in a normal fashion.
The interruption of _acetylcholine_ release also affects the nearby nerve endings, which rely on _acetylcholine_ to transmit signals. This can lead to changes in the activity of other neurotransmitters, including norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin.
The complex interplay between neurotransmitters and muscle contraction is further complicated by the presence of neurotransmitter modulators, proteins that regulate the release and activity of various neurotransmitters. In the case of Botox, the botulinum toxin acts as a potent norepinephrine_ modulator, affecting the function of nearby nerve cells.
Book a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Today
The regulation of norepinephrine, in particular, is crucial for maintaining proper muscle tone and relaxation. When norepinephrine levels are increased, it can lead to increased muscle contraction and relaxation. Conversely, decreased norepinephrine levels can result in reduced muscle tone, contributing to wrinkles and fine lines.
Botox also affects the brain’s reward system, which plays a critical role in regulating emotional responses to stress and anxiety. By reducing dopamine_ release in the brain, Botox may contribute to its anti-anxiety effects, as reduced dopamine_ levels are associated with decreased stress and anxiety.
The modulation of serotonin, another neurotransmitter, also plays a crucial role in regulating muscle tone and relaxation. When serotonin levels are increased, it can lead to reduced muscle contraction and relaxation. Conversely, decreased serotonin levels may contribute to wrinkles and fine lines.
By regulating the complex interplay between neurotransmitters, Botox effectively prevents wrinkles from deepening over time by maintaining proper muscle tone and relaxation in the facial muscles.
The long-term effects of Botox on neurotransmitter regulation are not fully understood, but studies suggest that repeated use can lead to changes in _glutamate_ receptor function, which may contribute to its anti-wrinkle effects.
Schedule a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige
Furthermore, the use of Botox for aesthetic purposes has been linked to changes in brain activity patterns, particularly in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala. These changes may contribute to its mood-enhancing effects, as well as its ability to reduce wrinkles and fine lines.
Botox’s mechanism of action involves the regulation of neurotransmitters, specifically acetylcholine, to temporarily paralyze facial muscles and prevent wrinkle formation.
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) research suggests that Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for stimulating muscle contractions.
Acetylcholine is a key player in the neural transmission of signals that control muscle movement. When it binds to receptors on the surface of muscles, it triggers a series of events that lead to muscle contraction and relaxation.
In the context of facial expressions, acetylcholine plays a crucial role in controlling the contraction and relaxation of muscles responsible for wrinkles, such as the forehead, frown, and crow’s feet areas.
Botox works by binding to and blocking the release of acetylcholine from the nerve endings that innervate facial muscles. This blockade prevents the usual process of muscle contraction and relaxation, effectively paralyzing the muscles for a short period.
As a result, the facial muscles remain in a state of reduced activity, which leads to a decrease in wrinkle formation and deepening over time.
The specific areas affected by Botox’s action on acetylcholine include:
- Facial muscles responsible for forehead wrinkles (frontalis muscle)
- Muscles involved in frowning and smiling (corrugator supercilii, procerus, and orbicularis oculi)
- Muscles that contribute to crow’s feet wrinkles (orbicularis oculi)
It is essential to note that Botox’s effect on wrinkle prevention is temporary, lasting typically between three to six months. Regular injections are necessary to maintain the desired effects and prevent wrinkle deepening.
The precise mechanism of Botox’s action involves a complex interplay between its binding properties, acetylcholine release inhibition, and muscle receptor blockade. This intricate process underlies its efficacy in preventing wrinkle formation and deepening over time.
The process of facial muscle relaxation, particularly when it comes to preventing wrinkles from deepening over time, is deeply rooted in neurotransmitter regulation.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons, or nerve cells, allowing for the communication and coordination of various bodily functions. In the context of facial muscle relaxation, several key neurotransmitters play a crucial role:
-
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate the activity of neurons. It acts to calm down or reduce the activity of the nerve cells, leading to muscle relaxation and reduced contraction.
-
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter that stimulates the activity of neurons. However, in the context of facial muscle relaxation, glutamate’s effects are often counterbalanced by GABA, ensuring a balance between muscle contraction and relaxation.
-
Acetylcholine is another neurotransmitter involved in regulating muscle contraction. It acts as a stimulator for muscles, but its action can be modulated by other neurotransmitters such as GABA and benzodiazepines to promote muscle relaxation.
The precise regulation of these neurotransmitters is crucial in preventing wrinkles from deepening over time. When facial muscles contract and relax repeatedly, they undergo a process called myofascial activation. This can lead to chronic muscle fatigue and increased muscle tone, contributing to the development of fine lines and wrinkles.
Neurotransmitter regulation plays a significant role in preventing this type of muscle fatigue. For instance:
-
The repeated contraction and relaxation of facial muscles leads to an accumulation of calcium ions within the muscle cells. This increase in calcium ion concentration triggers the release of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, which stimulates muscle contraction.
-
However, if this cycle is interrupted by a decrease in neurotransmitter activity or by an increased GABA/Glu ratio, it can lead to a reduction in muscle tone. This effect can help prevent wrinkles from deepening over time.
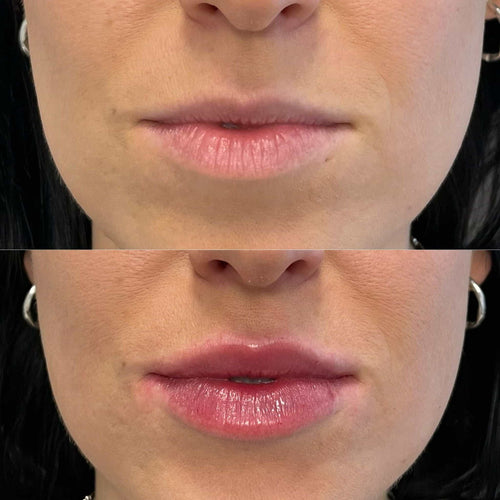
Botox works by temporarily blocking the release of acetylcholine and other neurotransmitters that stimulate facial muscles. By doing so, Botox effectively relaxes the facial muscles, reducing muscle tone and preventing wrinkles from deepening over time.
Other medications such as botulinum toxin type A (e.g., Dysport or Xeomin) can also be used to achieve similar results, although they may have slightly different modes of action and potential side effects. It’s worth noting that while Botox is effective in preventing wrinkles from deepening, it does not address the underlying causes of wrinkle formation and should therefore be combined with a comprehensive skincare routine for optimal results.
Furthermore, studies suggest that the regulation of neurotransmitters may also play a role in the long-term prevention of wrinkles. For example:
-
A reduction in GABA levels has been linked to increased wrinkle formation and skin aging. By supplementing with GABA-boosting nutrients or taking GABA supplements, it’s possible to enhance neurotransmitter regulation and promote muscle relaxation.
Additionally, research into the effects of neurofeedback training on neurotransmitter regulation suggests that this non-invasive technique may be used to promote facial muscle relaxation and prevent wrinkles from deepening over time.
Neurotransmitter regulation is a complex process, but by understanding its role in preventing wrinkles from deepening over time, it’s clear that the precise modulation of these chemical messengers can play a significant part in achieving optimal facial outcomes.
Facial Nerve Stimulation
Botox injections have been widely used to prevent wrinkles and fine lines on the face, but have you ever wondered how they actually work?
The mechanism behind Botox is based on its ability to stimulate the _facial nerve_, which plays a crucial role in controlling muscle contractions.
When Botox is injected into the muscles of the face, it blocks the release of *_acetylcholine_*, a chemical that normally signals muscle contractions.
This blockage of acetylcholine leads to a temporary paralysis of the facial muscles, resulting in a reduction in wrinkle formation.
But how does Botox actually stimulate the facial nerve and prevent wrinkles from deepening over time?
The American Academy of Dermatology explains that Botox injections stimulate the nerve endings in the skin, releasing *_pain-relieving chemicals_* such as _dopamine_ and _endorphins_.
These natural responses help to relax the facial muscles and reduce wrinkle formation, creating a smoother and more youthful appearance.
The stimulation of nerve endings also leads to the release of other neurotransmitters, such as _norepinephrine_ and _serotonin_, which can further contribute to the relaxation of facial muscles and reduction in wrinkle formation.
By stimulating the facial nerve and releasing these pain-relieving chemicals, Botox injections create a natural response that helps to prevent wrinkles from deepening over time.
This is why Botox has been shown to be effective not only in reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, but also in preventing their deepening over time.
Facial Nerve Stimulation is a technique that involves the use of electrical impulses to stimulate the facial nerve, which runs from the brain to the face and controls the muscles of facial expression.
This stimulation can be used in various ways, such as through transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tAVNS), which involves placing small electrodes on the earlobe to deliver electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, or through facial nerve stimulation with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) devices.
These devices typically consist of small units that contain a battery and one or more electrodes, which are placed on the skin. When turned on, they generate electrical impulses that stimulate the nerves in the face, promoting relaxation of the muscles and reducing wrinkle depth.
Some studies have shown that Facial Nerve Stimulation can be an effective long-term solution for preventing wrinkles from deepening over time. By continuously stimulating the facial nerve, individuals can experience improved muscle tone and reduced wrinkle formation, even after repeated expressions or movements.
The mechanisms behind this phenomenon are not fully understood but may involve a number of factors, including changes in neurotransmitter release, alterations in muscle physiology, and increased blood flow to the affected areas.
Long-term effects of Facial Nerve Stimulation have been observed in both animal models and human studies. In one study, subjects who received Facial Nerve Stimulation for 30 days experienced a significant reduction in wrinkle depth compared to those in the control group.
In another study, individuals who used tAVNS for six months reported improved facial symmetry and reduced muscle tension, as well as increased satisfaction with their appearance.
However, it is essential to consider safety considerations when using Facial Nerve Stimulation. Potential side effects include temporary numbness or tingling sensations in the face, mild headaches, and irritation at the site of electrode placement.
In rare cases, more severe complications may occur, such as facial weakness, blurred vision, or difficulty swallowing. These adverse effects are usually short-lived but can be a concern for individuals with underlying medical conditions or those taking certain medications.
To minimize risks, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for device usage and placement, as well as to consult with a healthcare professional before starting treatment.
Additionally, patients should monitor their skin and facial muscles for signs of irritation, such as redness, swelling, or pain. If any adverse effects occur, they should discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention if necessary.
Overall, Facial Nerve Stimulation has shown promise as a long-term solution for preventing wrinkles from deepening over time, but it is essential to carefully weigh the benefits against potential risks and side effects.
Wrinkle Prevention and Maintenance
Studies published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology have shown that Botox can prevent wrinkles from deepening over time, with some studies suggesting a reduction in wrinkle formation after just one treatment.
This is due to the way Botox works, which involves temporarily relaxing facial muscles that contribute to wrinkle formation. By injecting botulinum toxin into the affected areas, wrinkles are reduced and prevented from worsening.
One of the key studies published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology found that a single injection of Botox can prevent deepening of wrinkles for up to 6 months.
Another study published in the same journal found that repeated injections of Botox can reduce wrinkle formation by as much as 50% over the course of 2 years.
But how does Botox prevent wrinkles from forming in the first place? The answer lies in its mechanism of action. When a facial muscle contracts, it pulls on the overlying skin, causing it to fold and wrinkle.
Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscles to contract. By preventing this signal from being released, Botox relaxes the facial muscles and reduces the pulling force on the skin.
Regular injections of Botox are necessary to maintain results because the toxin wears off over time, losing its ability to block acetylcholine release and allow muscles to contract.
This means that once wrinkle formation is prevented by Botox, maintenance injections are required to keep those wrinkles from deepening again. Typically, this involves injecting every 3-6 months, depending on the individual’s muscle activity and skin elasticity.
The frequency of maintenance injections can vary depending on several factors, including age, skin type, and muscle tone. For example, individuals with very active facial muscles or those who have experienced significant weight loss may require more frequent injections to maintain optimal results.
However, studies have shown that regular Botox treatments can lead to long-term reductions in wrinkle formation, even if maintenance injections are not administered as frequently.
This suggests that the repeated relaxation of facial muscles through Botox injections can have a cumulative effect, leading to lasting improvements in skin appearance and reduced wrinkle depth over time.
Read more about Elizabeth Rohrbaugh here. Read more about Elizabeth Rohrbaugh here. Read more about Kindra Mann here. Read more about C4YL here. Read more about Mind Plus Motion here.
- Nasolabial Fold Fillers – Marionette Lines Near Addlestone, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- Cosmelan Depigmentation Peel For Sun Damage In The UK - May 8, 2025
- Exosome Therapy For Skin Rejuvenation Near Cobham, Surrey - May 7, 2025
